Understanding how your car’s HVAC system works can empower you to maintain it properly and troubleshoot issues. This guide delves into the inner workings of automotive HVAC systems, exploring the key components and their functions, common refrigerants used, and potential problems that may arise.
A car’s heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system provides comfort by regulating temperature and humidity inside the cabin. It operates by manipulating refrigerant, a special fluid, between liquid and gaseous states to absorb heat and release cool air. Let’s explore the process in detail.
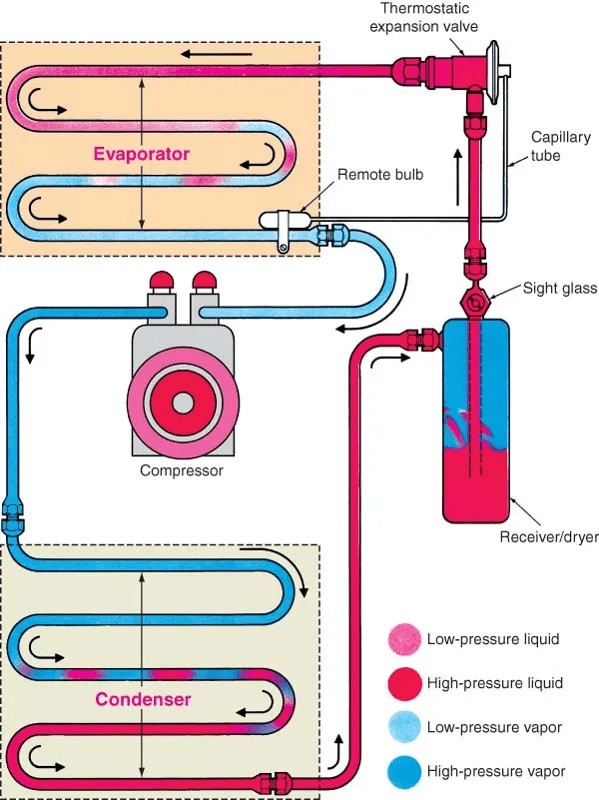
Understanding the Refrigeration Cycle
The core of the HVAC system lies in the refrigeration cycle. This cycle involves four key stages and components working in harmony:
1. Compression
The compressor, driven by the engine’s serpentine belt, takes in low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas. It then compresses this gas, increasing both its temperature and pressure significantly. This high-temperature, high-pressure gas then moves to the condenser.
 Car AC Compressor
Car AC Compressor
2. Condensation
The condenser, located at the front of the vehicle, resembles a radiator. As the hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas flows through the condenser, heat is dissipated to the surrounding air. This causes the refrigerant to cool down and condense into a high-pressure liquid.
3. Expansion
The high-pressure liquid refrigerant then passes through an expansion valve or orifice tube. This device restricts the flow of refrigerant, causing a sudden pressure drop. This pressure drop results in a significant temperature decrease, transforming the liquid refrigerant into a low-temperature, low-pressure mixture of liquid and gas.
4. Evaporation
Finally, the low-temperature refrigerant enters the evaporator, located inside the passenger compartment. As air blown by the blower motor passes over the evaporator coils, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the air and evaporates back into a gas. This heat absorption cools the air, which is then circulated into the cabin. The now gaseous refrigerant returns to the compressor, restarting the cycle.
Key Components of a Car HVAC System
Besides the core components involved in the refrigeration cycle, several other parts play crucial roles:
- Receiver/Dryer: This component removes moisture and contaminants from the refrigerant, protecting the system from damage.
- Blower Motor: This motor forces air across the evaporator and heater core, circulating conditioned air throughout the cabin.
- Heater Core: For heating, hot engine coolant flows through the heater core. The blower motor then blows air across the heater core, warming the air before it enters the cabin.
- Control System: This system allows the driver to adjust temperature, fan speed, and airflow direction. Modern systems often include automatic climate control for optimal comfort.
Refrigerants and Environmental Concerns
Over time, different refrigerants have been used in car AC systems. Older systems used R-12 (Freon), which was found to damage the ozone layer. R-134a replaced R-12, being more environmentally friendly. Currently, R-1234yf is becoming the new standard due to its lower global warming potential. Recharging a system requires specialized equipment and knowledge of the correct refrigerant type.
Common HVAC System Failures
Several issues can disrupt the efficient operation of a car’s HVAC system:
- Leaks: Refrigerant leaks are a common problem, leading to reduced cooling performance and potential compressor damage.
- Compressor Issues: The compressor, being the heart of the system, can fail due to leaks, electrical problems, or wear and tear.
- Condenser Blockage: Debris and dirt can restrict airflow through the condenser, hindering heat dissipation and reducing cooling efficiency.
- Electrical Malfunctions: Issues with wiring, sensors, or the control system can disrupt the HVAC system’s operation.
Conclusion
Understanding how your car’s HVAC system works allows you to better maintain it and address potential issues. Regular checks, timely repairs, and professional servicing can ensure a comfortable driving experience year-round. If you suspect any problems with your HVAC system, consult a qualified automotive technician for diagnosis and repair.

