Postoperative pain management is crucial for patient recovery and well-being. Leveraging technology through patient self-management tools, such as mobile applications, offers a promising approach to improving the efficiency and quality of care. This article examines the key organizational factors influencing the successful adoption of eHealth innovations, specifically focusing on tools that empower patients in managing their postoperative pain. Understanding these factors is essential for hospitals seeking to integrate technology effectively into their postoperative care pathways.
 alt text: A flow chart showing how absorptive capacity relates to mediating factors such as management support and organizational readiness.
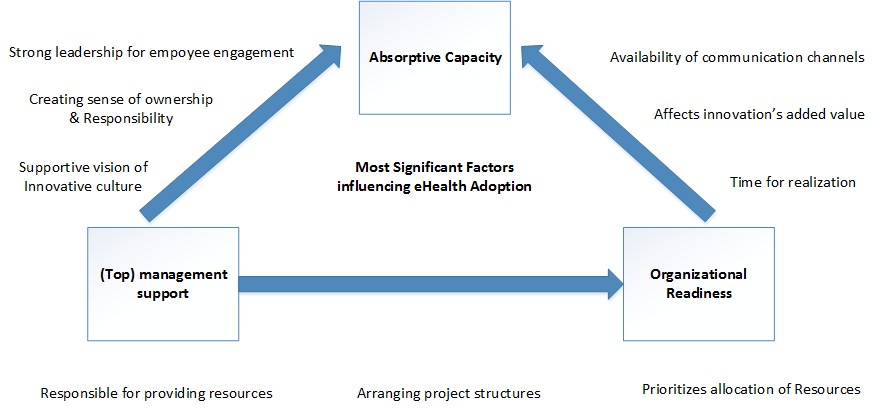
alt text: A flow chart showing how absorptive capacity relates to mediating factors such as management support and organizational readiness.
The Crucial Role of Absorptive Capacity
A hospital’s ability to adopt new technologies hinges on its “absorptive capacity,” which encompasses the organization’s capability to acquire, assimilate, transform, and apply new knowledge. This dynamic process is fundamental to leveraging the potential of eHealth innovations like patient self-management tools for postoperative care.
A key component of absorptive capacity is the willingness and ability of individual staff members to embrace new information and integrate it into their daily routines. Factors influencing this include:
- Personal characteristics: Age, tech affinity, and individual adopter type (early vs. late) can impact a person’s willingness to adopt new tools.
- Context: The perceived urgency and relevance of the problem the innovation addresses significantly affect adoption rates. If staff understand the tangible benefits for both patients and themselves, they are more likely to embrace the change.
- Sense of Ownership: Fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among staff is crucial. When individuals feel invested in the success of the innovation, they are more likely to actively participate in its implementation.
The Impact of Leadership and Organizational Readiness
While individual willingness is essential, organizational factors play a significant role in shaping absorptive capacity and ultimately, successful eHealth adoption.
- Management Support: Strong leadership support, from top management to team leaders, is crucial for providing resources, setting a clear vision, and fostering a culture of innovation. Active involvement of team leaders, who are directly involved in implementation, is particularly important.
- Organizational Readiness: This encompasses the hospital’s IT infrastructure, financial resources, and overall culture. While adequate IT infrastructure is essential, financial constraints can be overcome if the innovation demonstrates clear value and potential for improving patient care. A culture that encourages learning, adaptability, and open communication is crucial for successful adoption.
Practical Recommendations for Successful Implementation
To effectively integrate patient self-management tools for postoperative care, hospitals should focus on:
- Demonstrating Value: Clearly articulate the benefits of the innovation using the Quadruple Aim framework: lower costs, improved patient care, better health outcomes, and enhanced staff experience.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Involve all stakeholders, including clinicians, IT staff, and patients, from the outset. Employing a value-sensitive design approach fosters ownership and ensures the tool meets the needs of all users.
- Cultivating Leadership: Appoint leaders or “ambassadors” who can champion the innovation, provide guidance, and facilitate training. These individuals play a crucial role in overcoming resistance to change and fostering a positive culture around the new technology.
Conclusion: Empowering Patients Through Technology
Patient self-management tools hold immense potential for optimizing postoperative care. By focusing on absorptive capacity, fostering strong leadership support, and ensuring organizational readiness, hospitals can successfully implement these innovations and empower patients in their recovery journey. This proactive approach leads to improved patient outcomes, enhanced efficiency, and a more positive overall experience for both patients and healthcare providers.


