Looking for a reliable Multi Standard Car Scan Tool? This guide provides a practical introduction to On-Board Diagnostics (OBD2), the foundation for most car scan tools. We’ll cover the OBD2 connector, parameter IDs (PIDs), CAN bus communication, and practical tips for requesting and decoding OBD2 data.
What is OBD2 and Why Do You Need a Multi Standard Car Scan Tool?
OBD2 is your vehicle’s self-diagnostic system. It’s a standardized protocol enabling diagnostic trouble code (DTC) extraction and real-time data access via a multi standard car scan tool connected to the OBD2 port. This port, usually located near the steering wheel, allows the scan tool to communicate with the car’s computer.
A multi standard car scan tool is essential for:
- Diagnosing “Check Engine” Light: The dreaded malfunction indicator light signals an issue. A scan tool reads DTCs to pinpoint the problem.
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance: Access real-time data like speed, RPM, fuel levels, and more to understand your car’s performance.
- DIY Repairs and Maintenance: Diagnose issues yourself, potentially saving on costly mechanic visits.
OBD2 Standards and Protocols: What Your Scan Tool Needs to Support
OBD2 relies on several standards, making a multi standard car scan tool crucial. Key aspects include:
The OBD2 Connector (SAE J1962)
The 16-pin OBD2 connector provides access to vehicle data. Pin 16 (power) and pins 6 & 14 (CAN-H/L) are vital for common CAN bus communication.
OBD2 and CAN Bus (ISO 15765-4)
Since 2008, CAN bus is mandatory for OBD2 in US cars. ISO 15765-4 specifies communication details like bit-rates (250K/500K) and CAN identifiers (11/29-bit). Your multi standard car scan tool must handle these variations.
OBD2 Diagnostic Messages (SAE J1979, ISO 15031-5)
OBD2 messages contain modes (service types) and PIDs (specific parameters). Mode 0x01 requests current data, with numerous PIDs for various parameters.
ISO-TP for Longer Messages (ISO 15765-2)
ISO-TP handles messages exceeding the standard 8-byte CAN frame, crucial for data like VIN and DTCs. A multi standard car scan tool needs to understand this protocol.
Choosing the Right Multi Standard Car Scan Tool
Understanding OBD2 standards helps you select a suitable scan tool. Consider:
- Protocol Support: Ensure compatibility with various protocols (CAN, KWP2000, ISO 9141-2, J1850).
- Data Logging Capabilities: Choose a tool that can record data for later analysis if needed.
- Real-time Data Display: Clear and easy-to-understand data presentation is essential.
- Software and Updates: Regular software updates ensure compatibility with newer vehicles.
Decoding OBD2 Data: Making Sense of the Numbers
Raw OBD2 data requires decoding. SAE J1979 and ISO 15031-5 provide scaling information to convert raw values into meaningful units (e.g., km/h, °C). DBC files facilitate this process in software.
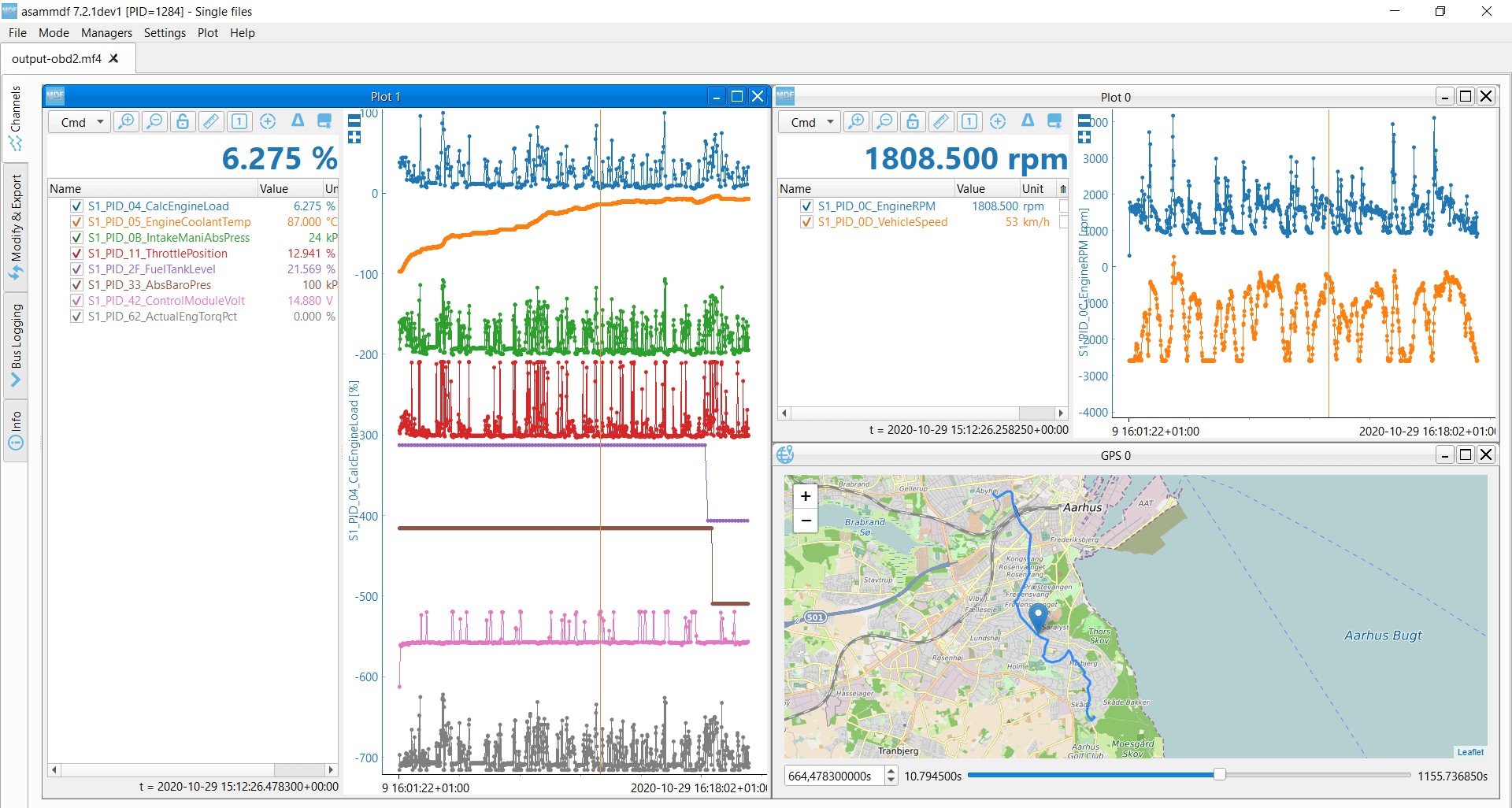 OBD2 data decoding example
OBD2 data decoding example
Future of OBD and Multi Standard Car Scan Tools
OBD standards are evolving:
- OBD3 and Telematics: Potential for remote diagnostics and emissions testing via wireless communication.
- Security Concerns: Increased focus on data security and preventing unauthorized access.
- Electric Vehicles: EVs present challenges with OEM-specific protocols (UDS) requiring specialized scan tools.
Conclusion: Empower Yourself with a Multi Standard Car Scan Tool
A multi standard car scan tool is invaluable for understanding and maintaining your vehicle. By understanding the underlying OBD2 standards and protocols, you can make an informed decision and utilize the tool effectively for diagnostics, maintenance, and performance monitoring. Select a tool that meets your needs and stay informed about evolving OBD technology.

