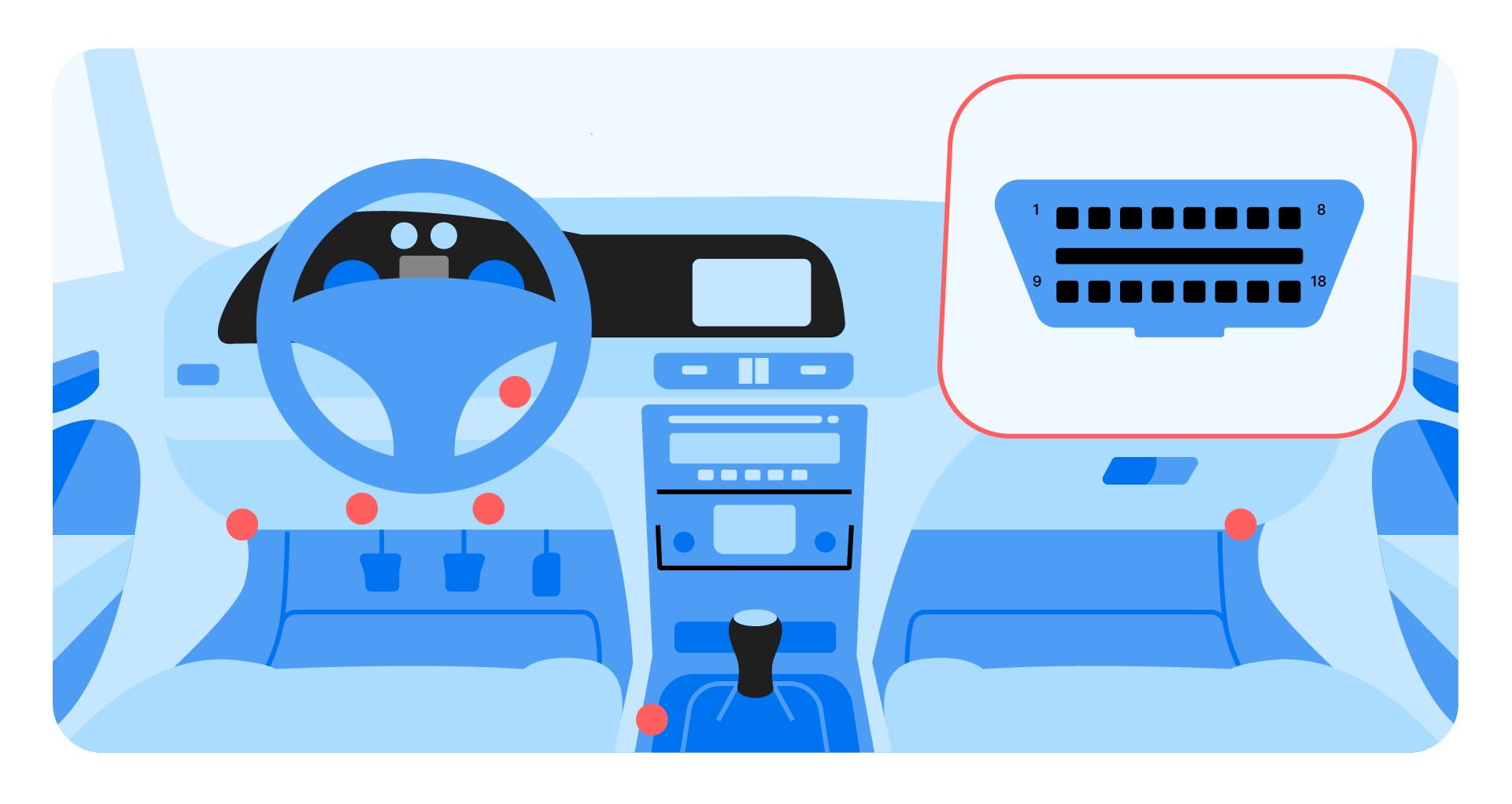
An OBD2 scanner is an essential tool for understanding your car’s health. By plugging into your car’s OBD port, it can reveal a wealth of information, helping you diagnose issues and potentially save on costly repairs. This guide will walk you through how to use an OBD2 scanner effectively.
Connecting Your OBD2 Scanner
Locating the OBD2 port is the first step. It’s typically found under the steering wheel or within the center console, often hidden by a plastic cover. Once located, connect your OBD2 scanner. Many modern scanners utilize Bluetooth, so ensure pairing is successful.
Powering Up and Vehicle Selection
With the scanner connected, turn the car’s ignition on. While some scanning can be done with the engine off, running the engine allows for live data readings. Next, select your car’s make, model, and specific details. This allows the scanner to correctly interpret the data. Many scanners offer automatic VIN recognition, simplifying this process.
Initiating the OBD Scan
Once the vehicle is identified, initiate the scan. You might have options to scan specific control units or perform a comprehensive scan of all systems. Consult your scanner’s manual if you encounter difficulties navigating the menu. A full scan can take anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes.
Interpreting OBD2 Fault Codes
The scan results will present a list of fault codes. These codes correspond to specific issues within your vehicle’s systems. Some codes are straightforward, indicating a specific component needing attention. For example, “00287 – ABS Wheel Speed Sensor; Rear Right” suggests a likely issue with that sensor.
However, other codes can be more ambiguous. “P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1)” indicates a lean fuel mixture, but the underlying cause could range from a clogged fuel filter to a failing fuel pump or various sensor issues.
Utilizing Live Data for Diagnostics
Beyond fault codes, many OBD2 scanners offer live data readings. This real-time information can be invaluable for diagnosing complex problems. For instance, if a car lacks power and only shows a limp mode fault code, examining live data for fuel pressure, boost pressure, and airflow can pinpoint the root cause.
Clearing Fault Codes after Repairs
After addressing a problem, rescan the system to ensure the fault code is gone. However, remember that fault codes are just a starting point. Always confirm the diagnosis with further testing to avoid unnecessary part replacements. Damaged wiring or loose connections can often trigger fault codes.
OBD2 Scanners for Used Car Inspections
OBD2 scanners are crucial when buying a used car. They can reveal hidden problems not readily apparent during a test drive. Combining a pre-purchase inspection with an OBD2 scan can help avoid costly surprises down the road.
Conclusion
Mastering how to use an OBD2 scanner empowers you to take control of your car’s maintenance. By understanding fault codes and leveraging live data, you can diagnose problems effectively, communicate more effectively with mechanics, and potentially save on repair costs. While some issues may still require professional attention, an OBD2 scanner provides valuable insight into your vehicle’s health.