An OBD2 scanner, also known as an OBD2 reader or code reader, is an essential tool for car owners and mechanics alike. It allows you to tap into your vehicle’s computer system, diagnose problems, and potentially save yourself a trip to the mechanic. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of how to work an OBD2 scanner.
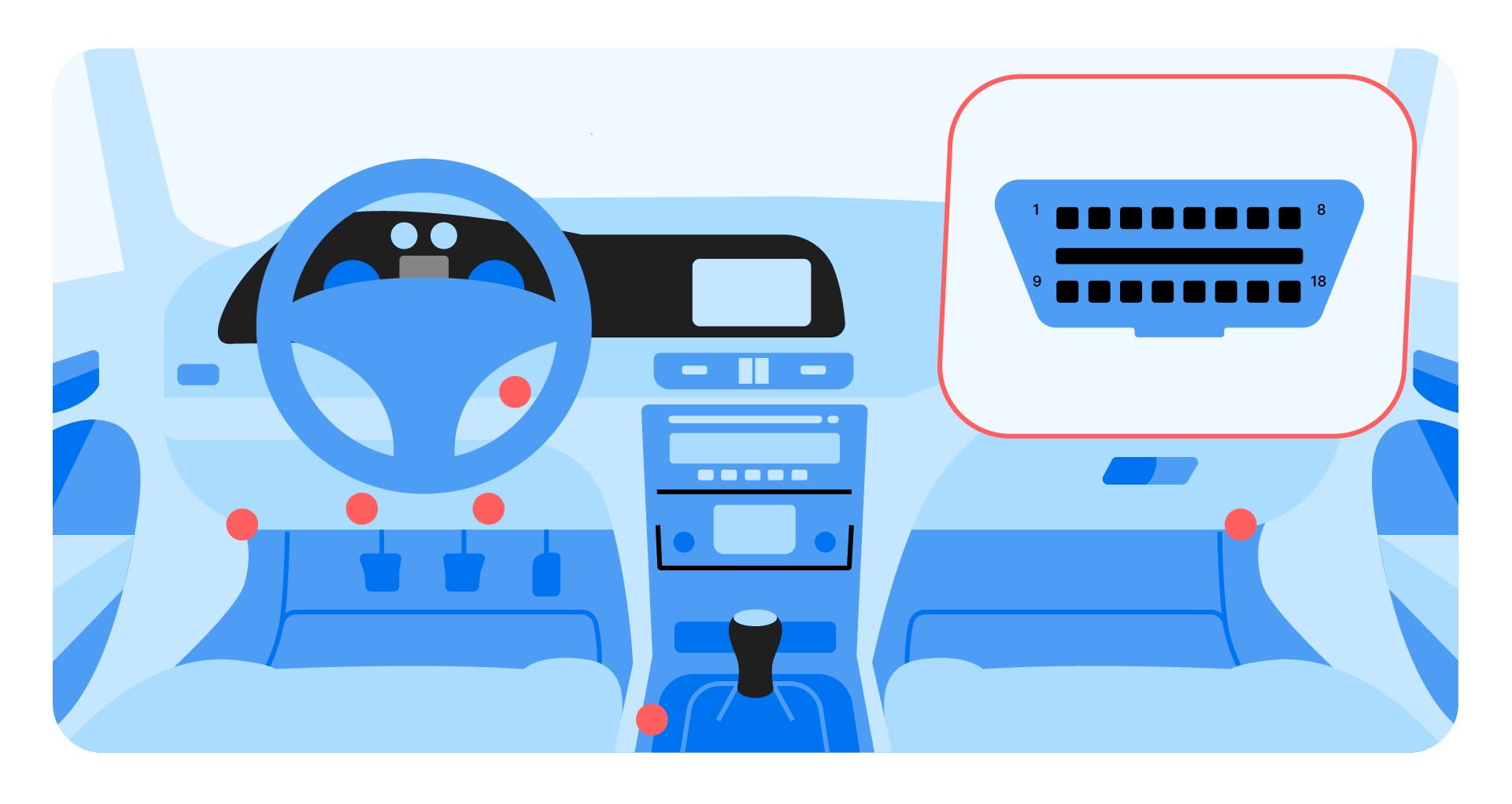
Typical OBD2 port location under the steering wheel.
Connecting the OBD2 Scanner
The first step in using an OBD2 scanner is locating the OBD2 port in your vehicle. This port is typically located under the dashboard, often near the steering column or center console. It’s a standardized 16-pin connector. Once you’ve located the port:
- Plug in the Scanner: Firmly insert the OBD2 scanner’s connector into the port. Ensure a secure connection. Bluetooth OBD2 scanners will require pairing with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth.
OBD2 scanner plugged into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position, but do not start the engine. This powers up the car’s computer and allows the scanner to communicate with it. For some functions, like viewing live data, the engine may need to be running.
Reading OBD2 Fault Codes
With the scanner connected and ignition on:
-
Select Vehicle Information: Some scanners require you to manually input your vehicle’s year, make, and model. Others automatically detect this information.
-
Initiate the Scan: Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Scan” function on your scanner or accompanying app. The scanner will then communicate with the car’s computer to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
-
Interpreting the Codes: The scanner will display a series of alphanumeric codes (e.g., P0300, P0420). These codes correspond to specific problems within the vehicle’s systems. Refer to a reliable OBD2 code database or your scanner’s manual to understand the meaning of each code. For instance, “P0420” typically indicates a problem with the catalytic converter system efficiency.
A mechanic using an OBD2 scanner.
Utilizing Live Data
Many OBD2 scanners offer the ability to view live data streams from various sensors in real-time. This feature is valuable for:
-
Monitoring Sensor Readings: Observe parameters such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and more. This helps pinpoint issues that might not trigger a fault code.
-
Troubleshooting Intermittent Problems: Live data can help diagnose problems that only occur under specific driving conditions.
Clearing Fault Codes
After addressing the underlying issue indicated by a fault code, you can use the OBD2 scanner to clear the code from the vehicle’s computer. This will turn off the check engine light and reset the monitoring system.
Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
OBD2 scanners range from basic code readers to advanced professional tools. Choose a scanner based on your needs and budget:
-
Basic Code Readers: Inexpensive and suitable for reading and clearing codes. Ideal for casual users.
-
Mid-Range Scanners: Offer live data, freeze frame data, and some advanced features. Suitable for DIY enthusiasts.
-
Professional Scan Tools: Provide comprehensive diagnostics, bi-directional control, coding capabilities, and more. Designed for professional mechanics.
Conclusion
Learning how to work an OBD2 scanner empowers you to take control of your vehicle’s maintenance and diagnose problems effectively. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply want to save money on repairs, understanding this essential tool is a valuable skill. Remember to consult reliable resources for interpreting fault codes and always address underlying issues before clearing codes.