Connecting to your 2003 Toyota Tacoma’s OBDII port is crucial for diagnostics and smog checks. If you’re having trouble connecting, this guide will walk you through common issues and solutions. While this article focuses on a 2012 model experience, the core principles and troubleshooting steps apply to a 2003 Tacoma as well.
Common OBD2 Connection Problems in a Tacoma
A non-responsive OBDII port can stem from several issues, often related to power supply, the port itself, or the scanning tool. Here are some common culprits:
Faulty OBD2 Scanner or Cable
The simplest explanation is often a faulty scanner or its connecting cable. Before delving into more complex troubleshooting, try a different scanner if possible. Borrow one from a friend or visit an auto parts store to test with a known working device.
Blown OBDII Fuse
The OBDII system in your Tacoma is protected by a fuse. Locate your vehicle’s fuse box (usually under the dash or in the engine bay) and consult your owner’s manual to identify the correct fuse for the OBDII system (likely labeled OBD or DLC). Visually inspect the fuse for damage or use a multimeter to test its continuity. Replace a blown fuse with the correct amperage. For a 2003 Tacoma, the OBDII fuse is likely a 7.5A fuse.
Wiring Issues
Damaged or corroded wiring between the OBDII port, fuse box, and the Engine Control Unit (ECU) can prevent communication. Visually inspect the wiring harness for any obvious signs of damage. A multimeter can be used to check for continuity in the wiring. This is a more advanced step that may require professional assistance.
ECU Problems
In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECU can prevent the OBDII port from communicating. This is a serious issue that requires professional diagnosis and repair.
Power Supply to the OBDII Port
Some OBDII scanners rely solely on the vehicle’s power supply through the port, while others have their own internal power source. A weak vehicle battery or a problem with the power supply pins in the OBDII port itself can prevent connection. Using a scan tool with its own power source can help diagnose this issue.
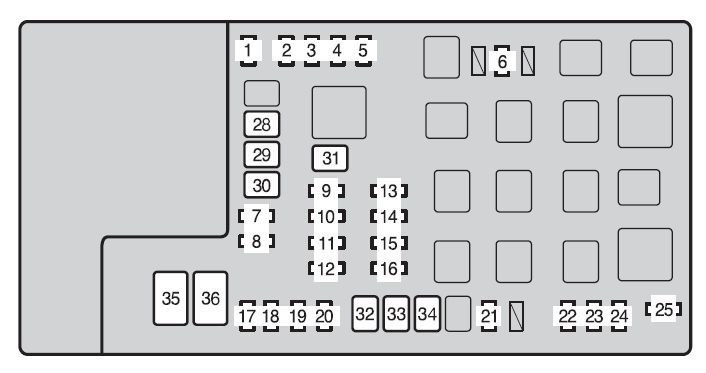 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Using a Powered OBD2 Scanner: A Potential Solution
Using a scan tool with its own independent power source often resolves connection problems. These scanners bypass the vehicle’s power supply through the OBDII port, eliminating that potential point of failure. Many professional-grade scan tools have built-in batteries.
Further Troubleshooting
If a powered scanner still doesn’t connect, consider these steps:
- Battery Disconnect: Disconnecting the vehicle’s battery for 30 seconds can sometimes reset the ECU and resolve communication issues.
- Professional Diagnosis: If all else fails, consult a qualified mechanic for professional diagnosis and repair. They have specialized tools and knowledge to pinpoint the problem accurately.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting a non-responsive OBDII port on your 2003 Toyota Tacoma often involves checking the fuse, scanner, and wiring. If these simple checks don’t resolve the issue, using a powered OBD2 scanner is a valuable diagnostic step. If problems persist, seeking professional help is recommended. A functioning OBDII port is essential for maintaining your Tacoma and ensuring it passes emissions tests.
